Glossary for Automotive SPICE®
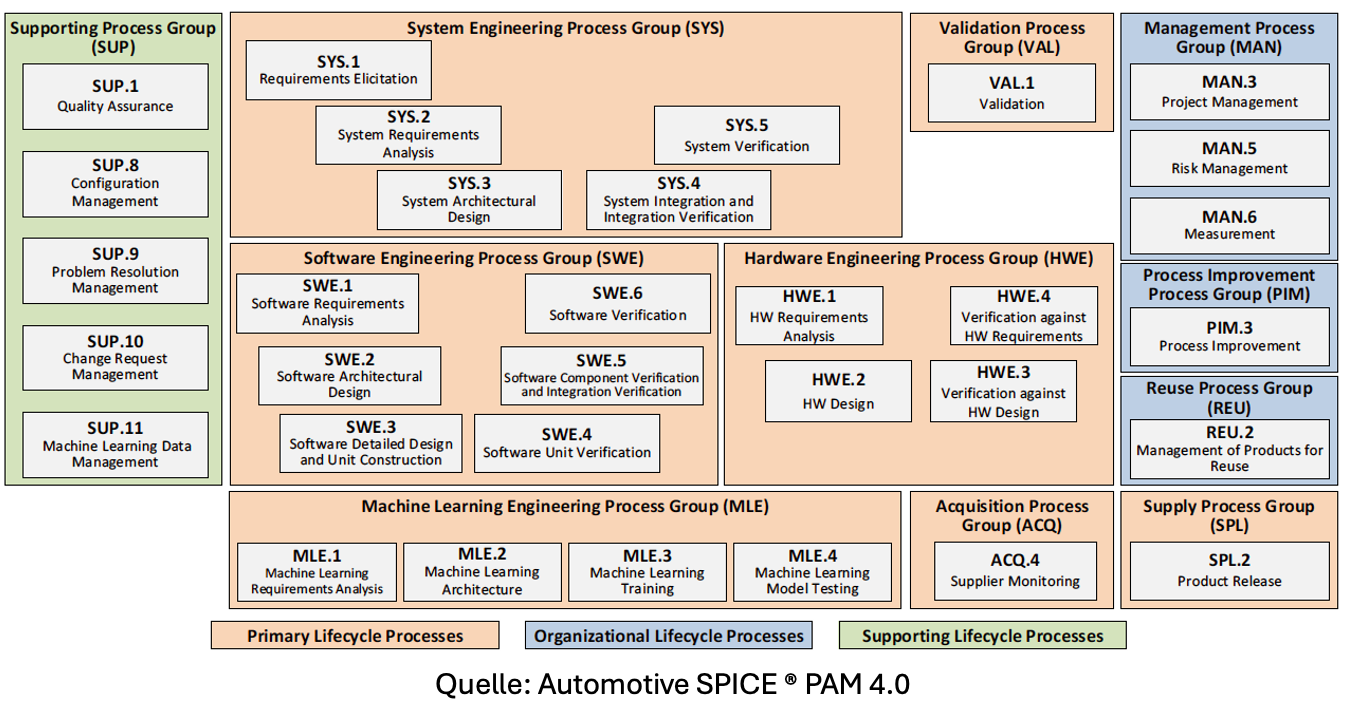
After explaining the basics of ASPICE in the last post, it is time to take a closer look at the terms of this framework:
The process model in ASPICE describes the structure and interaction between the various tasks performed during development. It provides guidance for planning, implementing, monitoring and evaluating the development process.
The maturity levels in ASPICE range from 0 to 5 and indicate the extent to which a company is able to implement the defined processes consistently and effectively. A higher maturity level indicates greater maturity and stability of the processes.
Process attributes in ASPICE include various aspects of process quality, such as the ability to plan, implement, monitor and improve the development process. It serves as a basis for evaluating and improving the company's performance.
Base Practices are specific activities or tasks that can be performed during development to meet ASPICE requirements. It is an important part of defined processes and helps companies implement proven processes and standards, as well as evaluate them in an assessment.
A "best practice" refers to a proven method, technique or approach that has been proven to be particularly effective and successful in practice. It is a recognized solution to a specific problem or challenge that is recommended by experts or organizations as a standard or reference. Best practices are often based on experience, knowledge and proven methods collected and documented in a specific field. They are designed to improve the efficiency, quality and results of processes, projects or activities by providing a guide to best practices.
Work products are products and artifacts created during development. These include specification documents, design specifications, test plans, implementation code, etc. The quality and processing of these work products will have a significant impact on the quality of the final product.
The process assessment in ASPICE is a formal process that evaluates the implementation of defined processes in the company. This is usually done by a special assessment team (assessors) based on the current process model.
An audit is a systematic review of a company's processes and products to ensure compliance with defined standards and guidelines. It can be assessed internally or externally and is used to identify weak points and suggest opportunities for improvement.
The difference between an "assessment" and an "audit" lies in the purpose, scope and implementation:
Assessment:
- Purpose: An assessment is designed to evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of a process, system or organization and to identify opportunities for improvement.
- Scope: An assessment can cover various aspects, such as processes, information items, base practices, etc.
- Implementation: Assessments are often carried out by internal or external professionals who meet specific requirements (certified assessors) to carry out the assessment.
- Result: The result of an assessment is usually a report or summary that contains the assessment results, identified strengths and weaknesses and recommendations for improvement.
Audit:
- Purpose: An audit is designed to verify compliance with standards, guidelines or regulations and to demonstrably ensure that the specified requirements are met.
- Scope: An audit typically focuses on reviewing specific processes, systems or activities, as well as documents or artifacts, to ensure that they comply with defined standards.
- Implementation: Audits are often conducted by internal or external auditors who meet specific requirements (certificates) to assess compliance with standards.
- Result: The result of an audit is usually an audit report that contains the results of the review, any identified conformities or non-conformities, and recommendations for corrective action, if any.
In summary, an assessment is a general evaluation of processes, while an audit is a specific verification of compliance with standards or regulations.
Improvement measures are concrete activities or tasks to optimize company processes and create a higher level of maturity. These measures are defined based on the results of the assessment and the feedback from the company.
In ASPICE, traceability is the ability to establish and track relationships and dependencies between artifacts during their development. This allows changes to be managed effectively and an overview of requirements, for example, to be maintained.
In ASPICE, consistency refers to the uniformity and coherence of the work products within a development project or across multiple projects. It is important that all processes and results are consistent with each other and do not contain any contradictions in order to ensure the efficiency and quality of development.
Generic practices in ASPICE are best practices or activities that can be applied to a variety of processes in different development projects. They are not specific to a particular process or phase, but serve as general guidelines for implementation in all processes.
Melster Consulting GmbH: Your experts for Automotive SPICE®
Take advantage of the opportunity to take your development processes to the next level today! Contact us to arrange an individual consultation. Find out how we at Melster Consulting GmbH can help you take advantage of ASPICE and achieve your goals. We look forward to working with you, understanding your requirements and developing customized solutions that promote your success.